
STXM-XANES analyses of carbonaceous matter in seafloor hydrothermal deposits from the ~3.5 Ga Dresser Formation in the North Pole area, Western Australia
ABSTRACT
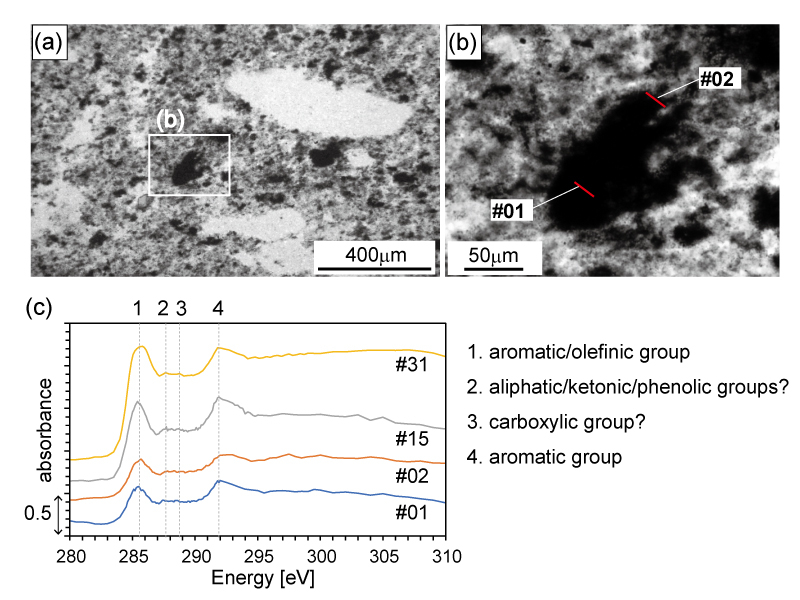
Carbonaceous matter (CM) in silica veins contained in the ~3.5 billion-year-old (Ga) Dresser Formation, Western Australia, can offer insights into biological activity in Earth’s oldest seafloor hydrothermal deposits, although a biological origin for this material remains debated. Herein, CM from Dresser hydrothermal vein deposits was analyzed using carbon X-ray absorption near edge structure (C-XANES) and Raman microspectroscopy. The CM is mainly composed of disordered aromatic structures, potentially containing minor aliphatic/ketonic/phenolic and carboxylic groups. These characteristics resemble those of biogenic Phanerozoic kerogen with high maturation, CM from the ~2.7 Ga Tumbiana Formation and the ~3.5 Ga Mount Ada Basalt in the Pilbara Craton, and abiotically synthesized graphite, but differ from those of CM produced via Fischer-Tropsch-type synthesis. Our observations indicate the presence of heteroatoms (hydrogen and possibly oxygen); however, the observed C-XANES spectra can be explained by either biotically or abiotically produced organic matter at this stage.
KEYWORDS
Keywords: Raman, STXM, C-XANES, Archean, carbonaceous matterSupplementary Materials(file)
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/geochemj/56/4/56_GJ22010/_supplement/_download/56_GJ22010_1.pdf
- Published : 2022
- Released on J-STAGE : 2022/08/26
- Received : 2022/01/05
- Accepted : 2022/07/15
- DOI : https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.GJ22010
- J-STAGE URL : https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/geochemj/56/4/56_GJ22010/_article/-char/en
- J-Online ISSN: 1880-5973
- Print ISSN : 0016-7002
- ISSN-L : 0016-7002
All Issues
- Vol.60, 2026
- Vol.59, 2025
- Vol.58, 2024
- Vol.57, 2023
- Vol.56, 2022
- Vol.55, 2021
- Vol.54, 2020
- Vol.53, 2019
- Vol.52, 2018
- Vol.51, 2017
- Vol.50, 2016
- Vol.49, 2015
- Vol.48, 2014
- Vol.47, 2013
- Vol.46, 2012
- Vol.45, 2011
- Vol.44, 2010
- Vol.43, 2009
- Vol.42, 2008
- Vol.41, 2007
- Vol.40, 2006
- Vol.39, 2005
- Vol.38, 2004
- Vol.37, 2003
- Vol.36, 2002
- Vol.35, 2001
- Vol.34, 2000
- Vol.33, 1999
- Vol.32, 1998
- Vol.31, 1997
- Vol.30, 1996
- Vol.29, 1995
- Vol.28, 1994
- Vol.27, 1993
- Vol.26, 1992
- Vol.25, 1991
- Vol.24, 1990
- Vol.23, 1989
- Vol.22, 1988
- Vol.21, 1987
- Vol.20, 1986
- Vol.19, 1985-1986
- Vol.18, 1984
- Vol.17, 1983
- Vol.16, 1982
- Vol.15, 1981
- Vol.14, 1980
- Vol.13, 1979
- Vol.12, 1978
- Vol.11, 1977
- Vol.10, 1976
- Vol.9, 1975
- Vol.8, 1974
- Vol.7, 1973
- Vol.6, 1972-1973
- Vol.5, 1971
- Vol.4, 1970-1971
- Vol.3, 1969-1970
- Vol.2, 1968
- Vol.1, 1966-1967




