
A new method for quantitative analysis of total water contents and estimating molecular water and hydroxyl contents in rhyolitic glasses by SIMS
ABSTRACT
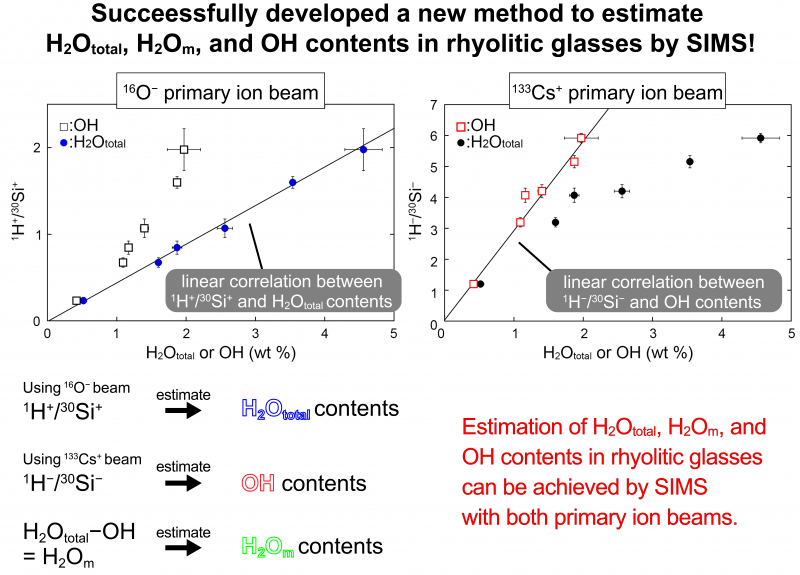
We have succeeded in developing a new analytical method to estimate the concentration of hydrous chemical species (molecular water; H2Om and hydroxyl groups; OH) and total water (H2Ototal) in rhyolitic glass using secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). This method makes it possible to estimate the H2Om contents, OH contents, and H2Ototal contents at the micrometer scale (<10 μm) in silicate glasses such as melt inclusions by SIMS. With a 16O– primary ion beam, a linear correlation between 1H+/30Si+ ratios and H2Ototal contents is observed. On the other hand, there is a linear correlation between 1H–/30Si– ratios and OH contents when using a 133Cs+ primary ion beam. These results suggest that the 1H+/30Si+ ratios reflect the H2Ototal contents, while the 1H–/30Si– ratios mainly reflect the OH contents. Therefore, the selective estimation of the H2Ototal or OH contents can be achieved through the selection of the primary ion beam (16O– and 133Cs+). This new method will aid in the estimation of the pressure and temperature of the magma reservoir in the Earth’s interior depending on the solubilities of H2Om, OH, and H2Ototal in silicate melts, and in the understanding of water transport in the silicate glasses and melts.
KEYWORDS
Keywords: SIMS, rhyolitic glass, water content, chemical species- Published : 2024
- Released on J-STAGE : 2024/05/03
- Received : 2023/12/21
- Accepted : 2024/03/18
- DOI : https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.GJ24008
- J-STAGE URL : https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/geochemj/58/3/58_GJ24008/_article/-char/en
- J-Online ISSN: 1880-5973
- Print ISSN : 0016-7002
- ISSN-L : 0016-7002
All Issues
- Vol.60, 2026
- Vol.59, 2025
- Vol.58, 2024
- Vol.57, 2023
- Vol.56, 2022
- Vol.55, 2021
- Vol.54, 2020
- Vol.53, 2019
- Vol.52, 2018
- Vol.51, 2017
- Vol.50, 2016
- Vol.49, 2015
- Vol.48, 2014
- Vol.47, 2013
- Vol.46, 2012
- Vol.45, 2011
- Vol.44, 2010
- Vol.43, 2009
- Vol.42, 2008
- Vol.41, 2007
- Vol.40, 2006
- Vol.39, 2005
- Vol.38, 2004
- Vol.37, 2003
- Vol.36, 2002
- Vol.35, 2001
- Vol.34, 2000
- Vol.33, 1999
- Vol.32, 1998
- Vol.31, 1997
- Vol.30, 1996
- Vol.29, 1995
- Vol.28, 1994
- Vol.27, 1993
- Vol.26, 1992
- Vol.25, 1991
- Vol.24, 1990
- Vol.23, 1989
- Vol.22, 1988
- Vol.21, 1987
- Vol.20, 1986
- Vol.19, 1985-1986
- Vol.18, 1984
- Vol.17, 1983
- Vol.16, 1982
- Vol.15, 1981
- Vol.14, 1980
- Vol.13, 1979
- Vol.12, 1978
- Vol.11, 1977
- Vol.10, 1976
- Vol.9, 1975
- Vol.8, 1974
- Vol.7, 1973
- Vol.6, 1972-1973
- Vol.5, 1971
- Vol.4, 1970-1971
- Vol.3, 1969-1970
- Vol.2, 1968
- Vol.1, 1966-1967




