
Photo-oxidation pathway as a potential CS2 sink in the atmosphere
ABSTRACT
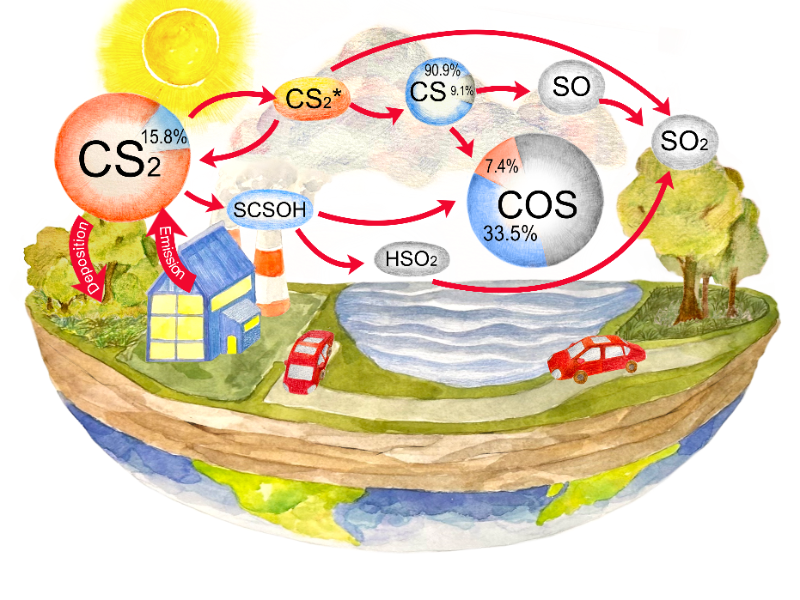
A 1D model of the CS2 reaction network with the addition of the photo-oxidation pathway has been developed and quantitatively studied. The reaction pathway analysis focusing on the sulfur element was applied to determine the importance of the photo-oxidation pathway in the atmospheric CS2 sink resulting in a 15.8% of sulfur in the CS2 reaction network passes through the photo-oxidation pathway under a global average solar radiation conditions and ranging from 8.1% to 18% depending on the irradiance intensity. The concentration of COS and SO2, the main products of CS2 atmospheric oxidation, changed slightly from the sulfur cycle developed with the updated CS2 reaction network. 7.4% of the COS comes from the new pathway and a total of 40.9% of COS comes from the conversion of CS2. A sulfur budget for the main species in the sulfur cycle was constructed, and the CS2 lifetime was estimated to be 2–3 days. The newly added photo-oxidation pathway plays an moderate role in the CS2 reaction network and has a high variability under specific geochemical conditions. The results of this report should be taken as an incentive for 3D climate-chemistry models to account for local COS sources.
KEYWORDS
Keywords: planetary atmospheres, atmospheric modeling, carbon disulfide, photooxidation, reaction pathway analysis- Published : 2024
- Released on J-STAGE : 2024/09/03
- Received : 2023/12/22
- Accepted : 2024/06/09
- DOI : https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.GJ24014
- J-STAGE URL : https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/geochemj/58/5/58_GJ24014/_article/-char/en
- J-Online ISSN: 1880-5973
- Print ISSN : 0016-7002
- ISSN-L : 0016-7002
All Issues
- Vol.60, 2026
- Vol.59, 2025
- Vol.58, 2024
- Vol.57, 2023
- Vol.56, 2022
- Vol.55, 2021
- Vol.54, 2020
- Vol.53, 2019
- Vol.52, 2018
- Vol.51, 2017
- Vol.50, 2016
- Vol.49, 2015
- Vol.48, 2014
- Vol.47, 2013
- Vol.46, 2012
- Vol.45, 2011
- Vol.44, 2010
- Vol.43, 2009
- Vol.42, 2008
- Vol.41, 2007
- Vol.40, 2006
- Vol.39, 2005
- Vol.38, 2004
- Vol.37, 2003
- Vol.36, 2002
- Vol.35, 2001
- Vol.34, 2000
- Vol.33, 1999
- Vol.32, 1998
- Vol.31, 1997
- Vol.30, 1996
- Vol.29, 1995
- Vol.28, 1994
- Vol.27, 1993
- Vol.26, 1992
- Vol.25, 1991
- Vol.24, 1990
- Vol.23, 1989
- Vol.22, 1988
- Vol.21, 1987
- Vol.20, 1986
- Vol.19, 1985-1986
- Vol.18, 1984
- Vol.17, 1983
- Vol.16, 1982
- Vol.15, 1981
- Vol.14, 1980
- Vol.13, 1979
- Vol.12, 1978
- Vol.11, 1977
- Vol.10, 1976
- Vol.9, 1975
- Vol.8, 1974
- Vol.7, 1973
- Vol.6, 1972-1973
- Vol.5, 1971
- Vol.4, 1970-1971
- Vol.3, 1969-1970
- Vol.2, 1968
- Vol.1, 1966-1967




